Technology is not a babysitter
Week1
- Curriculum and technology must be aligned.
- Control technology or it will control you.
- Balance happiness when you are outcomes driven.
- am I ready for an LMS? (learning management system)
- Are students ready for an LMS?
- What LMS do I choose? (Blackboard, and Schoology, Moodle free, Google Classroom free)
- How do I use an LMS
Week 2
The nine categories of technology come to us from educational technology experts, Pitler, Hubbell, and Kuhn
- Word processing applications (word processing and word cloud generators )
- organizing and brainstorming software (Webspiration, Inspiration, SMART Tools)
- data collection and analysis (Google Forms, SurveyMonkey, Poll Everywhere, classroom clickers)
- communication and collaboration software (Skype, FaceTime, TypeWith.Me, Facebook, Twitter)
- instructional media (BrainPOP, Discovery Education Streaming, Khan Academy, TEDx, TED Talks)
- multimedia creation (PowerPoint Prezi, Keynote, VoiceThread, iMovie, blogs, and vlogs)
- instructional interactives (MathBoard, Voxie, EnglishCentral, Duolingo)
- database and reference resources (Wikipedia, Wolfram|Alpha, Gapminder, RubiStar)
- kinesthetic technology (Nintendo Wii, Xbox Kinect, GPS.)
Six teaching events based loosely on Robert Gagne's Events of Instruction.
- Event one, stimulate background information. This is often called a warm-up or attention-getter, and is done not only to see what students already know but to introduce students to the new theme.
- Event two, organize and manage information. While this may be done at any point in a lesson, often teachers, after or during the warmup, give an indication of the major objectives of the instruction. Gagne calls this informing learners of the objectives.
- Event three, giving instruction. This portion of the lesson plan is intended to present new information. It is often scaffolded, meaning that it is presented in bite sized chunks, meant to help learners retain the information.
- Event four, practice and collaboration. This portion of time in a classroom students spend time trying to understand and practice the concepts taught. It is sometimes done in stages as well. Meaning that students may go from easier to more complex problems, or from guided to independent tasks.
- Event five, produce and demonstrate proficiency. Generally at the end of a practice period students demonstrate their skills and understanding. This may be for example in front of a class in the form of a presentation, in the form of an essay or often in the form of a test or quiz.
- Event six, assessment and feedback. Teachers in this final stage or event must now assess the presentation, essay or test and give feedback to the learner. The learner may be given an opportunity to revise or re-test their skills. Or an instructor, seeing what students did or did not understand may begin the cycle of instruction yet again.
Week 3
COIK. clear only if known 写的只有知道此事的人看得懂
Digital nativity: A digital native is someone who is simply born with technology around them.
- Learner 1: non-digital native, put them in pairs, create tutorials and provided guided activities.
- Leaner 2, digital native, limit distractions and set clear boundaries. Use a pomodoro.
- Learner 3. digital native, Slow down, go over portions of assignment sheet during the activity to make sure they're on task.
Week 4
integrating technology into their classroom.
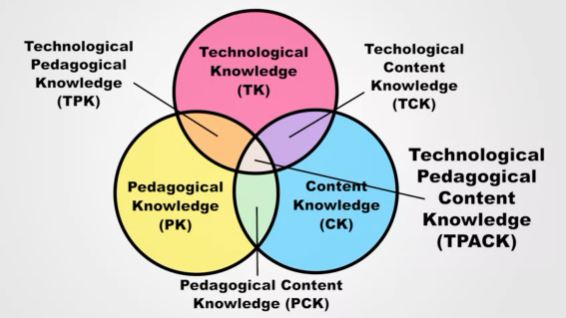
- Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge, TPACK
- Substitution Augmentation Modification and Redefinition, SAMR
what to teach, how to teach it and what technology to use in order to do it effectively
- content knowledge. This is knowing what to teach.
- pedagogical knowledge. This is knowing how to teach.
- technological knowledge. This refers to a teacher's understanding of technology, and how it can be applied to specific situations.
This is called redefinition. And example of this would be asking students to review the list of media resources that we provided, evaluate the information and then develop their own video presentation on the topic.
modification stage. Where we change the learning task because of the possibilities that technology provides. In this stage, instead of just reading from a textbook, we might give students, a list of media resources where they can obtain information. And have them decide which information is important and construct knowledge about the topic on their own.
Week 5
Reject Vendor, select your tools
- First, remember your objective
- Second, remember SAMR.
- Third, find early adopters.
- My fourth and final bit of advice is simple, become curious.
Find your objectives. Evaluate technology using SAMR. Use early adopters to help you discover and evaluate technologies. And above all, be curious.
These principals come from a man named Richard Mayor
the point we want to make is that technology itself can exert its own influence on the information that you are trying to relay to learners. It can truthfully change, transform the nature of the instruction itself.
imagine, design, transform. I dare you.









No comments:
Post a Comment